Step-by-step explanation:
(a) The given reaction equation is as follows.
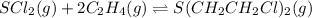
The given data is as follows.
Volume of the flask (V) = 5.0 L
Temperature (T) = (20.0^{o}C + 273.15) = 293.15 K
Number of moles of
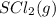 = 0.258 mol
= 0.258 mol
Number of moles of
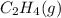 = 0.592 mol
= 0.592 mol
Number of moles of
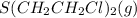 at equilibrium = 0.0349 mol
at equilibrium = 0.0349 mol
Hence, calculate the partial pressures of each given quantity using the ideal gas law formula as follows.
PV = nRT
or, P =
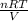
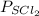 =
=
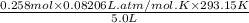
= 1.24 atm
Similarly,
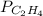 =
=
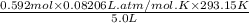
= 2.848 atm
Also,
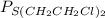 (equiiibrium) =
(equiiibrium) =
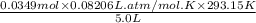
= 0.168 atm
For the reaction,
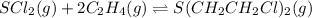
Initial : 1.241 2.848 0
Change : -x -2x +x
Equilibrium : (1.241 - x) (2.848 - 2x) x
Therefore, calculate partial pressure of each gas at equilibrium as follows.
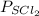 = 1.241 - x
= 1.241 - x
= (1.241 - 0.168)
= 1.073 atm
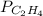 = 2.848 - 2x
= 2.848 - 2x
=
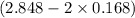
= 2.512 atm
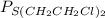 = x = 0.168 atm
= x = 0.168 atm
(b) The equilibrium constant for the reaction will be as follows.
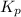 =
=
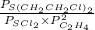
=
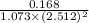
= 0.0248
= 0.025 (approx)
Therefore, K at
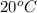 is 0.025 (approx).
is 0.025 (approx).