Answer:185.18 meV/m
Step-by-step explanation:
Energy loss for charge particle is given by
\frac{\mathrm{d} E}{\mathrm{d} x}\propto \frac{\rho Zz^2}{A}
where
\frac{\mathrm{d} E}{\mathrm{d} x} Energy loss per unit length
\rho density
Z atomic number
A atomic mass
z charge of incident particle(for proton it is 1)
For graphite
Z=6
A=12
For gaseous nitrogen
Z=7
A=14
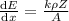
For graphite
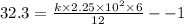
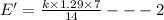
Divide 1 and 2
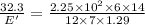
E'=185.18 MeV/m