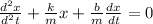Answer:
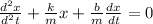
Step-by-step explanation:
The spring mass equation for the damped oscillation will be,
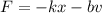
Here, -bv is the damping term used in this b is damping constant, k is spring constant, x is elongation in the spring, F is the force.
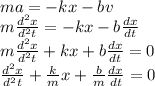
Therefore the differential equation for the damped harmonic oscillator is,