Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that molarity of acetic acid = 0.0100 M
Therefore, moles of acetic acid = molarity of acetic acid × volume of buffer
Moles of acetic acid = 0.0100 M × 1.00 L
= 0.0100 mol
Similarly, moles of acetate = molarity of sodium acetat × volume of buffer
= 0.100 mol
When
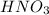 is added, it will convert acetate to acetic acid.
is added, it will convert acetate to acetic acid.
Hence, new moles acetic acid = (initial moles acetic acid) + (moles
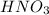 )
)
= 0.0100 mol + x
New moles of sodium acetate = (initial moles acetate) - (moles
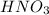 )
)
= 0.100 mol - x
According to Henderson - Hasselbalch equation,
pH =
![pK_(a) + log([conjugate base])/([weak acid])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/raol1rs3nhf4fgwwl5hd8vnp836804kg38.png)
pH =
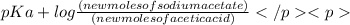
4.95 = 4.75 +
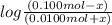
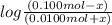 = 4.95 - 4.75
= 4.95 - 4.75
= 0.20
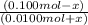 = antilog (0.20)
= antilog (0.20)
= 1.6
Hence, x = 0.032555 mol
Therefore, moles of
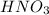 = 0.032555 mol
= 0.032555 mol
volume of
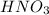 =
=
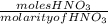
=
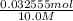
= 0.0032555 L
or, = 3.25 (as 1 L = 1000 mL)
Thus, we can conclude that volume of
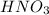 added is 3.26 mL.
added is 3.26 mL.