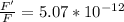Answer:
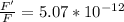
Step-by-step explanation:
given data:
surface temperature 7300 K
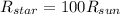
we know that
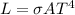
Where
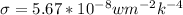
A area of illuminated surface
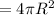
T = temperature of surface
WE KNOW THAT
![(L)/(L_O) = [(R)/(R_(sun))]^2+[(T)/(T_(sun))]^4](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/college/giitq9na3gvzuvp6pdra1fecqc8u5rj877.png)
T = 7300 K
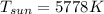
![(L)/(L_O) = 100^2 * [(7300)/(5778)]^4](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/college/2icr3fmwib9x3rng0dihoo0tm5quln1xzp.png)
L = L_O * 2.54*10^4
WE KNOW THAT
r = 1 parsec, pc = 3.085*10^{16] m
luminosity decrease when move away from the core
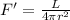
![= (L)/(4 \pi R^2) *[(R)/(r)]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/college/7vf6tn0hzarbjf793xeznfe25u6eei4a4h.png)
![F' = F *[(R)/(r)]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/college/34djc3immotep3z63np05ef5hhiu8m1psg.png)
![(F')/(F) = [(6.95)/(3.085)]^2*10^(-12)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/college/xnqqyfbrefl9a4ej7iv950o8peeqzbbgc0.png)