Answer:
Option A is the Answer.
Step-by-step explanation:
Treatment of alkyne with Bromine in the presence of
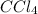 produces a trans product that is, a alkenyl bromide.
produces a trans product that is, a alkenyl bromide.
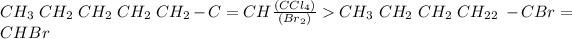
E-1, 2-dibromoheptene
It is a trans intermediate on further halogenations produces a tetrabromopentane.
It is an electrophilic expansion response in which the triple bond breaks to turn into a twofold bond and creates a dibromoalkene (E-1,2 dibromoheptene), and on further expansion, the twofold bond turns into a solitary bond and delivers a tetrabromoalkane.