By using Stokes's theorem to the required (VxF).dS is 26π.
Given that,
Function F(x, y, z) = -13yzi + 13xzj +4(x2 + y2)zk .
And S is the part of the paraboloid z = x2 + y2 that lies inside the cylinder x2 + y2 = 1, oriented upward. JS.
We have to determine,
Use Stokes' theorem to evaluate (V x F).dS.
According to the question,
By using Stokes's theorem to evaluate (V x F).dS .
F(x, y, z) = -13yzi + 13xzj +4(x2 + y2)zk .
Stokes' theorem says the integral of the curl of over F is s equal to the integral of F along the boundary of S , with counterclockwise orientation (when viewed from above).
This boundary is the circle
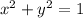 set in the plane
set in the plane
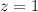 .
.
Then,
The parameterize path is given by the,
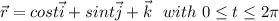
Then,
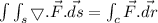
![= \int^(2\pi )_0 (-13sint\vec{i} + 13cost\vec{j} +4\vec{k} ) . (-sint\vec{k} + cost\vec{j}).dt\\\\= \int^(2\pi )_0 (13sin^2t +13cos^2t)dt\\\\= 13\int^(2\pi )_0 1.dt \\\\=13 [{t}]^(2\pi )_0\\\\= 13 [ 2\pi -0] \\\\= 13*2\pi \\\\=26\pi](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/qqqv8fy1xb6t8cx10jz3qzm3r5sapt50fe.png)
Hence, By using Stokes's theorem to the required (VxF).dS is 26π.
To know more about Integration click the link given below.