Step-by-step explanation:
- A bond formed due to transfer of electron from a less electronegative atom to a more electronegative atom is known as an ionic bond.
For example, in NaCl there is large electronegativity difference between Na and Cl. As a result, chlorine being more electronegative will attract valence electron of Na.
Hence, there will be development of partial positive charge on Na and partial negative charge will develop on Cl.
An ionic bond will always form between a metal and a non-metal.
- On the other hand, a covalent bond is formed by sharing of electrons. Non-metals that have great difference in electronegativity tend to form polar covalent bond.
For example, in HCl there will be a formation of a polar covalent bond as sharing of electron is taking place between H and Cl.
And, due to electronegativity difference there will be partial positive charge on H and partial negative charge on chlorine.
- A pure covalent bond is defined as a bond formed by sharing of electrons between non-metals that have very small or zero electronegativity difference.
For example,
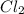 is a pure covalent compound as there is zero electronegativity difference between both Cl atoms.
is a pure covalent compound as there is zero electronegativity difference between both Cl atoms.
Thus, we can conclude that order of increasing difference in electronegativity will be as follows.
pure covalent bond < polar covalent bond < ionic bond