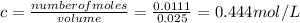Answer:
0.444 mol/L
Step-by-step explanation:
First step is to find the number of moles of oxalic acid.
n(oxalic acid) =
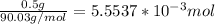
Now use the molar ratio to find how many moles of NaOH would be required to neutralize
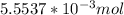 of oxalic acid.
of oxalic acid.
n(oxalic acid): n(potassium hydroxide)
1 : 2 (we get this from the balanced equation)
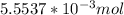 : x
: x
x = 0.0111 mol
Now to calculate what concentration of KOH that would be in 25 mL of water: