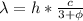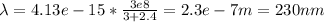Answer:
2.4 eV
230 nm
Step-by-step explanation:
The equation for the photoelectric effect is:
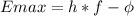
Where
h: Planck's constant (4.13e-15 eV * s)
f: frequency
phi: work function
This can be omdified to:
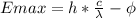
Where
c: speed of light in vacuum
lambda: wave length
We can set two equations:
(1)

(2)
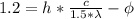
If we multiply equation (2) by 1.5 we obtain
(3)
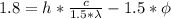
If we substract eq (3) from eq (1)
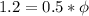
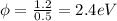
Knowing this we can calculate the original wavelength