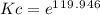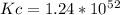Answer:
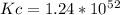
Explanation: For the given reaction:
![Kc=([Zn^+^2])/([Ag^+]^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/qgrwwec7vuyww5gpkr3k7wjgz9ccd81x5w.png)
Concentrations of the ions are not given so we need to think about another way to calculate Kc.
We can calculate the free energy change using the standard cell potential as:
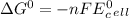
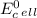 can be calculated using standard reduction potentials.
can be calculated using standard reduction potentials.
Standard reduction potential for zinc is -0.76 V and for silver, it is +0.78 V.
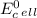 =
=
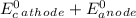
Reduction takes place at anode and oxidation at cathode. As silver is reduced, it is cathode. Zinc is oxidized and so it is anode.
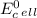 = 0.78 V - (-0.76 V)
= 0.78 V - (-0.76 V)
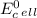 = 0.78 V + 0.76 V
= 0.78 V + 0.76 V
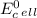 = 1.54 V
= 1.54 V
Value of n is two as two moles of electrons are transferred in the cell reaction F is Faraday constant and its value is 96485 C/mol of electron .
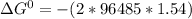
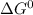 = -297173.8 J
= -297173.8 J
Now we can calculate Kc using the formula:
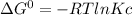
T = 25+273 = 298 K
R =
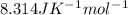
--297173.8 = -(8.314*298)lnKc
297173.8 = 2477.572*lnKc
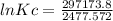
lnKc = 119.946