Step-by-step explanation:
According to the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
pH =
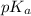 +
+
![(log[A^(-)])/([HA])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/fvyzdh4kfgzpyg0wsvk34eamguellxhfza.png)
Given values are pH = 6,
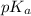 = 8
= 8
Putting given values into the above equation as follows.
6 = 8 +
![(log [A^(-)])/([HA])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/yxrlm5m6a8uobp9uwnezvi0g5wf1c9ohlm.png)
![(log[A^(-)])/([HA])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/fvyzdh4kfgzpyg0wsvk34eamguellxhfza.png) = -2
= -2
![([A^(-)])/([HA])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/aqob76gnk5at0cs1bms0w0c2gm6z8849is.png) = antilog -2
= antilog -2
= 0.01
But according to the question, we need protonated to deprotonated ratio of
![([HA])/([A^(-)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/wxftk31fgsskluimqhafgdgvb05h94veqd.png)
![([HA])/([A^(-)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/wxftk31fgsskluimqhafgdgvb05h94veqd.png) =
=
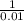
![([HA])/([A^(-)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/wxftk31fgsskluimqhafgdgvb05h94veqd.png) = 100
= 100
Thus, we can conclude that ratio of the protonated to the deprotonated form of the acid is
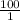 .
.