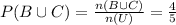Answer:
Given information: U = {E1, E2, E3, E4, E5}, A = {E1, E2} B = {E3, E4} C = {E2, E3, E5}
Total number of outcome = 5
From the given information, we get
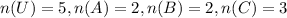
Formula for probability:
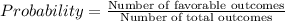
(a)
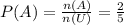
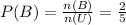
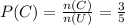
(b)
We need to find P(A U B) if A and B are mutually exclusive.
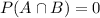
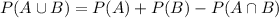
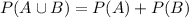
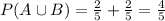
(c)
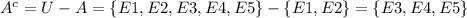
Number of elements in
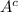 = 3
= 3
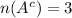
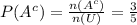
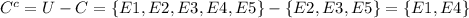
Number of elements in
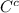 = 2
= 2
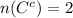
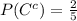
(d)
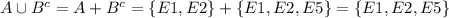
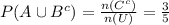
(e)
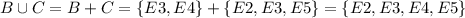
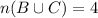
So,