Answer:
C) 80 milliamperes
Explanation:
The amount of current flowing through a circuit is directly proportional to the amount of voltage applied across the circuit. The relation between current(I) and voltage(V) can be expressed as:
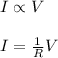
Here,
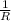 is the proportionality constant. It is given that, when voltage is 2 volts, 40 milliamperes(
is the proportionality constant. It is given that, when voltage is 2 volts, 40 milliamperes(
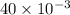 amperes) current flow through the circuit. Using these values we can find the value of proportionality constant. i.e.
amperes) current flow through the circuit. Using these values we can find the value of proportionality constant. i.e.
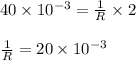
Using this value, we can establish the relation between I and V as:
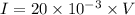
Now, we need to calculate value current (I) if voltage is equal to 4 volts. Substituting V = 4 in above equation, we get:
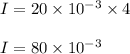
Thus, the value of current will be 80 milliamperes