Step-by-step explanation:
When there occurs a decrease in oxidation state of an element then it means the element has been reduced.
Whereas when there occurs an increase in oxidation state of an element then it means the element has been oxidized.
As the given reaction is as follows.
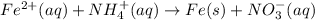
Oxidation state of iron is changing from +2 to 0. It means iron is getting reduced.
On the other hand, oxidation state of N in
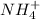 is as follows.
is as follows.
x + 4(1) = +1
x = 1 - 4
= -3
Hence, oxidation state of N in
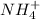 is -3.
is -3.
Oxidation state of N in
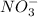 is as follows.
is as follows.
x + 3(-2) = -1
x - 6 = -1
x = +5
Hence, oxidation state of N in
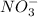 is +5. It means nitrogen is being oxidized.
is +5. It means nitrogen is being oxidized.
Thus, we can conclude that nitrogen is the element which is being oxidized in the given reaction.