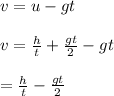Answer:
1) The initial velocity equals
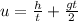
2) The velocity with which the keys were caught equals
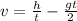
Step-by-step explanation:
Let the keys be thrown with a speed 'u' vertically upwards. Since the keys are caught after time 't' while covering a distance 'h' we can use second equation of kinematics to relate these terms.
According to second equation of kinematics the displacement of an object in 't' time is given by
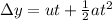
Applying the corresponding values and solving for the initial speed 'u' we get
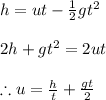
The change in velocities while covering a distance 's' can be found from first equation of kinematics
Thus we have
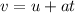
Applying corresponding values we get