Answer : The molar mass of an acid is 266.985 g/mole
Explanation : Given,
Mass of an acid (HX) = 4.7 g
Volume of NaOH = 32.6 ml = 0.0326 L
Molarity of NaOH = 0.54 M = 0.54 mole/L
First we have to calculate the moles of NaOH.
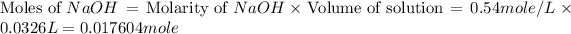
Now we have to calculate the moles of an acid.
In the titration, the moles of an acid will be equal to the moles of NaOH.
Moles of an acid = Moles of NaOH = 0.017604 mole
Now we have to calculate the molar mass of and acid.
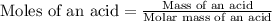
Now put all the given values in this formula, we get:
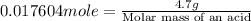
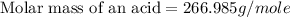
Therefore, the molar mass of an acid is 266.985 g/mole