Answer:
option e, 18.7 J/K
Step-by-step explanation:
Volume of C6H6 = 7.61 mL
Density of C6H6 = 0.879 g/mol
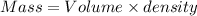
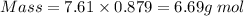
No. of mol = Mass in g/Molecular mass
No. of mol of benzene = 6.69/78 = 0.086 mol
Volume of oxygen = 22.3 L
No. of moles of oxygen will be calculated using PV = nRT
Where,
P = 1 atm, V = 22.3 L, R = 0.0821 L · atm/(K · mol, T = 298 K
n = PV/RT
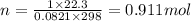
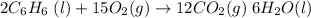
From reaction stoichiometry,
2 moles of benzene react with 15 moles of O2
0.086 mole of benzene will react with
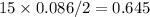 mol of O2
mol of O2
Since, 0.911 mol of O2 is present in reaction mixture, therefore O2 will not be the limiting reagent.
So the limiting reagent of the reaction will ne C6H6.
2 moles of C6H6 reacts with O2, then change in entropy is –437.7 J/K
0.086 mole of C6H6 reacts with O2 and change in entropy
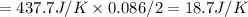
so, the correct will be option e.