Answer:
The standard heat of formation of Compound X at 25°C is -3095.75 kJ/mol.
Step-by-step explanation:
Mass of compound X = 7.00 g
Moles of compound X =
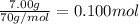
Mass of water in calorimeter ,m= 35.00 kg = 35000 g
Change in temperature of the water in calorimeter = ΔT
ΔT = 2.113°C
Specific heat capacity of water ,c= 4.186 J/g °C
Q = m × c × ΔT
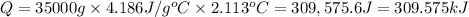
Heat gained by 35 kg of water is equal to the heat released on burning of 0.100 moles of compound X.
Heat of formation of Compound X at 25°C:
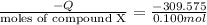
= -3095.75 kJ/mol