Answer: Option (B) is the correct answer.
Step-by-step explanation:
An equilibrium reaction is defined as the reaction in which the rate of forward reaction is equal to the rate of backward reaction.
For example,
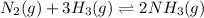
Whereas if a chemical reaction does not have rate of forward reaction equal to the rate of backward reaction then it is not known as an equilibrium reaction.
For example,
 is not an equilibrium reaction.
is not an equilibrium reaction.
Thus, we can conclude that the statement rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction, correctly describes any chemical reaction that has reached equilibrium.