Answer:
23.0733 L
Step-by-step explanation:
The mass of hydrogen peroxide present in 125 g of 50% of hydrogen peroxide solution:
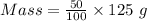
Mass = 62.5 g
Molar mass of
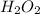 = 34 g/mol
= 34 g/mol
The formula for the calculation of moles is shown below:
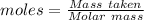
Thus, moles are:
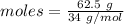
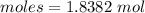
Consider the given reaction as:
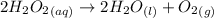
2 moles of hydrogen peroxide decomposes to give 1 mole of oxygen gas.
Also,
1 mole of hydrogen peroxide decomposes to give 1/2 mole of oxygen gas.
So,
1.8382 moles of hydrogen peroxide decomposes to give
![\frac {1}{2}* 1.8382 mole of oxygen gas. </p><p>Moles of oxygen gas produced = 0.9191 mol</p><p>Given: </p><p>Pressure = 746 torr </p><p>The conversion of P(torr) to P(atm) is shown below: </p><p>[tex]P(torr)=\frac {1}{760}* P(atm)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/t3x6zp7hst3ss4f8n6awkgp261e2po4882.png)
So,
Pressure = 746 / 760 atm = 0.9816 atm
Temperature = 27 °C
The conversion of T( °C) to T(K) is shown below:
T(K) = T( °C) + 273.15
So,
T₁ = (27 + 273.15) K = 300.15 K
Using ideal gas equation as:
PV=nRT
where,
P is the pressure
V is the volume
n is the number of moles
T is the temperature
R is Gas constant having value = 0.0821 L.atm/K.mol
Applying the equation as:
0.9816 atm × V = 0.9191 mol × 0.0821 L.atm/K.mol × 300.15 K
⇒V = 23.0733 L