Answer:
Approximately
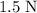 , assuming that the ice surface is level, the puck is moving, and that
, assuming that the ice surface is level, the puck is moving, and that
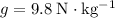 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
With a mass of
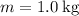 , the weight of this puck would be
, the weight of this puck would be
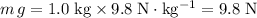 (downward in the vertical direction.)
(downward in the vertical direction.)
The question stated that the push on the puck is horizontal. If the ice surface is level, the friction on the puck would also be horizontal. At the same time, the normal force on this puck would be vertical. The only forces on this puck in the vertical direction would be the normal force and the weight of the puck.
Since the puck is not moving vertically, the forces in the vertical direction (normal force and the weight of the puck) must be balanced. Thus, the normal force on this puck would be opposite to the weight of this puck. The magnitude of the normal force
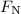 on this puck would be equal to the magnitude of the weight of the puck,
on this puck would be equal to the magnitude of the weight of the puck,
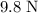 .
.
The question states that the coefficient of kinetic friction is
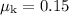 between the ice and the puck. If the puck is moving, the magnitude of the friction between the ice and this puck would be
between the ice and the puck. If the puck is moving, the magnitude of the friction between the ice and this puck would be
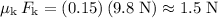 .
.