Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that,
Sound intensity level,
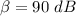
Area of eardrum,
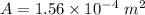
Time taken, t = 9 hours = 32400 s
Sound intensity level is given by :
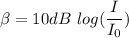
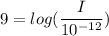
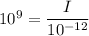
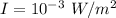
Sound intensity is given by :
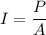
And P = E/t
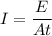
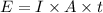
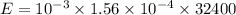
E = 0.00505 Joules
or
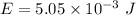
So, the incident energy on the eardrum during this time is
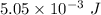 . Hence, this is the required solution.
. Hence, this is the required solution.