Step-by-step explanation:
As it is given that air is compressed steadily from 150 kPa and 300 K to 600 KPa with a mass flow rate of 5 kg/s.
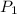 = 150 kPa,
= 150 kPa,
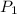 = 600 kPa
= 600 kPa
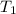 = 300 K,
= 300 K,
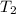 = ?
= ?
Mass flow rate (m) = 5 kg/s.
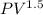 = constant
= constant
Q = 50.35 kJ/kg, n = 1.5
(a) Calculate the exit temperature of air as follows.
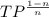 = constant
= constant
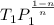 =
=
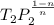
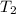 =
=
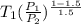
=
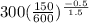
= 476.22 K
(b) An energy balance equation for the compressor and determine its power input in kW as follows.
Q - w = m (\Delta H + K.E + P.E)
As K.E and P.E will be negligible here. So, Q and w will be in kW.
Also,
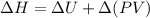
 =
=
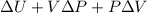
As, Q - w =

and
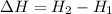
So, air enthalpy at 150 kPa and 300 K,
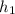 = ?
= ?
Air enthalpy = 1.007 \times T(q) - 0.026
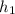 =
=

= 27.163 kJ/kg
Also,
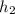 =
=
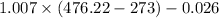
= 204.62 kJ/kg
Q = mQ
=
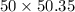
= 251.75 kJ/s
Q - w =
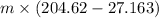
- w = 887.285 - 251.75
= -635.535 kJ/s
or, = 635.535 kW
Whereas negative sign indicates that work is done on the system.