Answer : The correct option is, (C) 0.090
Solution : Given,
Initial moles of
 = 0.350 mole
= 0.350 mole
volume of solution = 5.00 L
First we have to calculate the concentration
 .
.
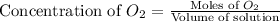
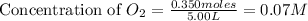
The given equilibrium reaction is,
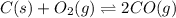
Initially 0.07 0
At equilibrium (0.07-x) 2x
The expression of
 will be,
will be,
![K_c=([CO]^2)/([O_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/4lrxgzxq22suxet8tfk9tnsf0k2a2td1gu.png)
As we are given the concentration of
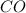 at equilibrium is, 0.060 M
at equilibrium is, 0.060 M
That means,
2x = 0.060 M
x = 0.030 M
The concentration of
 at equilibrium = 0.07 - x = 0.07 - 0.03 = 0.04 M
at equilibrium = 0.07 - x = 0.07 - 0.03 = 0.04 M
Now put all the given values in the above expression, we get:
![K_c=([CO]^2)/([O_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/4lrxgzxq22suxet8tfk9tnsf0k2a2td1gu.png)
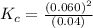
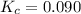
Therefore, the value of equilibrium constant for this reaction is, 0.090