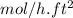Step-by-step explanation:
Transfer of mass A into stagnant film B depends on the availability of driving force.
Whereas driving force is the pressure difference at the surface of A and the bulk.
As,
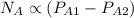
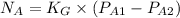
Therefore, putting the given values into the above formula as follows.
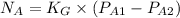
=
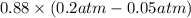
= 0.132
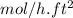
Thus, we can conclude that the flux of A from a surface into a mixture of A and B is 0.132