Answer:
R=
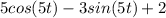
Explanation:
Using partial fraction decomposition to get a simpler denominator for the inverse transform:
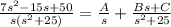
Multiple both sides by
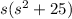
![[s(s^2+25)]\left[(7s^2-15s+50)/(s(s^2+25))\right ]=\left[ (A)/(s)+(Bs+C)/(s^2+25)\right ][s(s^2+25)]\\7s^2-15s+50=A(s^2+25)+(Bs+C)s\\7s^2-15s+50=As^2+25A+Bs^2+Cs](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/jd70oy88vj5apap4kwr18af8m8nkwkxbfc.png)
Separate in equations by grouping by the degree of the s:
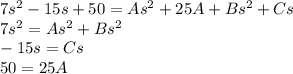
Solving for A and C:
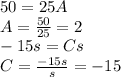
Substitute the value of A in the first separated equation to find the value of B:
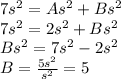
Returning to the partial fraction decomposition:
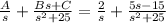
Applying the inverse Laplace transform:
![\mathcal{L}^(-1)\left[(2)/(s)+(5s-15)/(s^2+25)\right]=\mathcal{L}^(-1)\left[(2)/(s)\right]+\mathcal{L}^(-1) \left[(5s)/(s^2+25)\right]+\mathcal{L}^(-1)\left[(-15)/(s^2+25)\right]\\](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/d9zomvmnh2ubqah7trfg17ij1f07rcvlal.png)
![\mathcal{L}^(-1) \left[(2)/(s)+(5s-15)/(s^2+25)\right]=2\mathcal{L}^(-1)\left[(1)/(s)\right]+5\mathcal{L}^(-1) \left[(s)/(s^2+5^2)\right]-15\mathcal{L}^(-1)\left[(1)/(s^2+5^2)\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/5ci98z8bka48r2z9bhz17oc3r3snv1rdr4.png)
Using the next formulas:
![\mathcal{L}^(-1)\left[(1)/(s)\right]=1,\mathcal{L}^(-1) \left[(s)/(s^2+b^2)\right]=cos(bt),\mathcal{L}^(-1)\left[(1)/(s^2+b^2)\right]=(sin(bt))/(b)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/hnssrl5q6e2k2jgzb4pzxytloumeppsisz.png)
![\mathcal{L}^(-1)\left[(2)/(s)+(5s-15)/(s^2+25)\right]=2(1)+5cos(5t)-15((sin(5t))/(5) )\\\mathcal{L}^(-1)\left[(2)/(s)+(5s-15)/(s^2+25)\right]=2+5cos(5t)-3sin(5t)}\\\mathcal{L}^(-1)\left[(2)/(s)+(5s-15)/(s^2+25)\right]=5cos(5t)-3sin(5t)}+2](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/ct7z86tvz6439sc2dru7ca6dwgyrk3c11h.png)