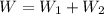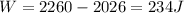Answer:
W = 234 J
Step-by-step explanation:
Initial volume of air is given as
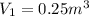
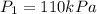
finally it is expanded isothermally to new pressure of 101.3 kPa
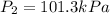
now by isothermal expansion we know
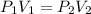
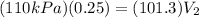
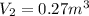
So work done in above process is given as
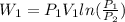
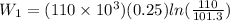
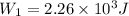
Now it is cooled to initial volume at constant pressure
so here in this case work done is given as
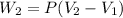
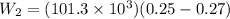
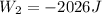
Now total work done is given as