Answer:
a) 30.20 m/s
b) 12.91 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
Mass of squirrel = 575 g = m
Drag coefficient = 0.70 = C
Density of air = 1.21 kg/m³ = ρ
frontal surface area = 0.0146 m² = A
Height the squirrel falls = 8.5 m = h
a) Drag force
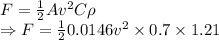
This force will oppose gravity
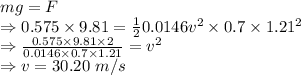
∴ Terminal velocity is 30.20 m/s
b) Neglecting drag force we get
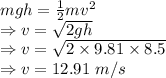
∴ Velocity of a 56 kg person falling that distance, assuming no drag contribution is 12.91 m/s