Answer:
The hydroxide ion
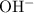 is the conjugate base in this equation.
is the conjugate base in this equation.
Step-by-step explanation:
The acid and base in a conjugate pair differ only by a proton
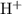 . As the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory goes, the substance with that extra proton
. As the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory goes, the substance with that extra proton
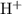 is considered to be the acid. The other substance in the pair is considered to be the base.
is considered to be the acid. The other substance in the pair is considered to be the base.
In this reaction, there are two conjugate acid-base pairs:
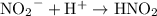 :
:
- Base:
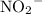 , which accepts a proton;
, which accepts a proton; - Acid:
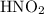 .
.
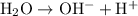 :
:
- Acid:
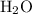 , which supplies a proton;
, which supplies a proton; - Base:
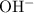 .
.
By convention, an acid A reacts with a base B to produce
- a conjugate base of A, and
- a conjugate acid of B.
In other words,
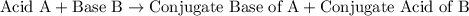 .
.
For this reaction,
- Acid A is
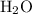 , and
, and - Base B is
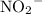 .
.
On the right-hand side of the equation:
- The Conjugate Base of A is
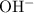 , and
, and - The Conjugate Acid of B is
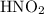 .
.