Answer: Expression for equilibrium constant kp is
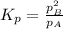 and equilibrium concentration of B is 0.141 atm.
and equilibrium concentration of B is 0.141 atm.
Explanation: Equilibrium expression is written as:
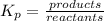
Note: for Kp, we use the partial pressures where as for Kc, we use the concentrations.
If we look at the given reaction then, the reactant is A and the product is B. Coefficient of B is 2 so we will do the square of B and the equilibrium expression will be:
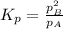
small p stands for partial pressures.
If change in pressure is x then the equilibrium pressure of A will be (20-x) atm and the equilibrium pressure of B will be 2x atm.
Let's plug in the values in the equilibrium expression:
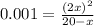
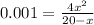
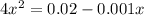
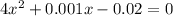
This is a quadratic equation. On solving this equation:
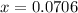
So, equilibrium pressure of B = 2(0.0706) atm = 0.141 atm