Answer: The rate of heat flow is 3.038 kW and the rate of lost work is 1.038 kW.
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given:
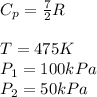
Rate of flow of ideal gas , n = 4 kmol/hr =
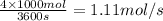 (Conversion factors used: 1 kmol = 1000 mol; 1 hr = 3600 s)
(Conversion factors used: 1 kmol = 1000 mol; 1 hr = 3600 s)
Power produced = 2000 W = 2 kW (Conversion factor: 1 kW = 1000 W)
We know that:
 (For isothermal process)
(For isothermal process)
So, by applying first law of thermodynamics:
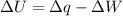
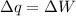 .......(1)
.......(1)
Now, calculating the work done for isothermal process, we use the equation:
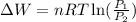
where,
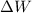 = change in work done
= change in work done
n = number of moles = 1.11 mol/s
R = Gas constant = 8.314 J/mol.K
T = temperature = 475 K
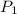 = initial pressure = 100 kPa
= initial pressure = 100 kPa
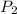 = final pressure = 50 kPa
= final pressure = 50 kPa
Putting values in above equation, we get:
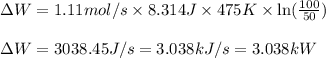
Calculating the heat flow, we use equation 1, we get:
[ex]\Delta q=3.038kW[/tex]
Now, calculating the rate of lost work, we use the equation:
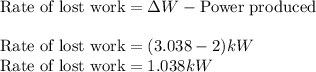
Hence, the rate of heat flow is 3.038 kW and the rate of lost work is 1.038 kW.