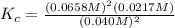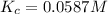Answer:
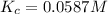
Explanation: The given chemical reaction is:
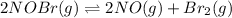
Equilibrium constant (Kc) in general is written as:
![K_c=([products])/([reactants])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/vw72w9tfn7zwox7bu3r0clwjokaxfr9qca.png)
Note:- Coefficients are written as their powers
So, the Kc expression for the above reaction will be:
![K_c=([NO]^2[Br_2])/([NOBr]^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/k4096gwdp3fzrtbueuvcfhq64iqldvh8kd.png)
Equilibrium moles are given for all of them. Let's divide the moles by given liters to get the concentrations.
![[NOBr]=(0.412mol)/(10.3L)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/7pqvhj42olfnfwa8tgd194e0omeqf68txm.png) = 0.040 M
= 0.040 M
![[NO]=(0.678mol)/(10.3L)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/lnpuev8kdlfhrucxy3b1imsegt2in68fo8.png) = 0.0658 M
= 0.0658 M
![[Br_2]=(0.224mol)/(10.3L)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/2sjtuq7cdk037091euc9nk2k1g7o90qgc8.png) = 0.0217 M
= 0.0217 M
Plug in the values in the equilibrium expression to calculate Kc.