Answer:
- It is the amount of energy released or absorbed when a substance is formed by a synthesis chemical reaction.
- Reaction in which a fuel is burned with oxygen to yield water and carbon dioxide (among others).
- It is the amount of energy released when a fuel is burned.
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
1. Standard heat of formation is understood as the involved energy, say absorbed or released, when a chemical compound is formed at STP conditions. For instance, formation of water:
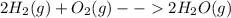
Releases 286kJ per 1 mole of formed water, that is why its standard heat of formation is
 .
.
2. Combustion chemical reactions consist on the reaction between a fuel, usually a hydrocarbon, and oxygen to yield carbon dioxide and water was shown below, for example, for ethane:
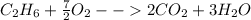
3. Standard heat of combustion is understood as the involved energy, surely released, when a fuel is burned with oxygen at STP conditions. For instance, for the aforesaid combustion of ethane the standard enthalpy of combustion has a value of
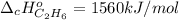
Best regards.