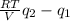Step-by-step explanation:
Let inlet flow rate =
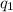
and, outlet flow rate =
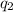
Also, it is known that
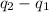 =
=
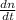 ....... (1)
....... (1)
where, n = number of moles accumulating in tank
According to ideal gas equation, PV = nRT
Hence, P =
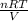
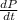 =
=
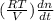
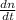 =
=
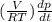
As it is given that T and V are constant. Hence, from equation (1) and (2) we get the following.
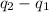 =
=
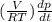
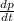 =
=