Step-by-step explanation:
The given data is as follows.
n = 2,
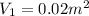 ,
,
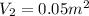
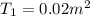 = 300 K ,
= 300 K ,
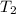 = 500 K
= 500 K
P = 1 bar
Equation for work done will be as follows.
W =

=
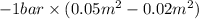
= - 3000 J
Hence, formula for heat added is as follows.
Q =
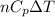
Putting given values into the above formula as follows.
Q =
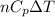
=
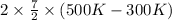
= 11639.6 J
Thus, we can conclude that the amount of heat added is 11639.6 J.