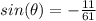Answer:
Part 1)
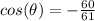
Part 2)
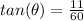
Part 3)
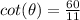
Part 4)
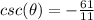
Part 5)
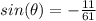
Explanation:
we know that
If angle theta lie on Quadrant III
then
The function sine is negative
The function cosine is negative
The function tangent is positive
The function cotangent is positive
The function cosecant is negative
The function secant is negative
step 1
Find
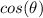
we know that
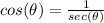
we have
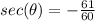 ----> the value must be negative
----> the value must be negative
therefore
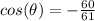
step 2
Find
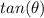
we know that
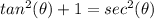
we have
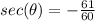
substitute
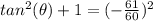
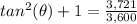
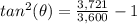
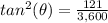
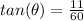
step 3
Find
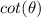
we know that
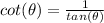
we have
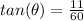
therefore
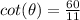
step 4
Find
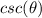
we know that
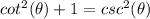
we have
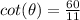
substitute
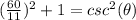
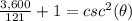
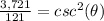
square root both sides
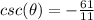
step 5
Find
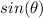
we know that
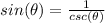
we have
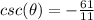
therefore