Answer:
Option B. doubles
Step-by-step explanation:
This can be explained by the definition of capacitance that charge on the capacitor will remain constant irrespective of the voltage applied.
This can be given as:
Q ∝ V or Q = CV
where,
Q = charge
V = Voltage
C = Capacitance
So, when V is doubled, C shoul reduce to half to main constant charge on the capacitor:
V' = 2V
C' =
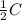
Also , Energy stored in a capacitor, E is given by:
E =
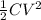 (1)
(1)
Now, when
V' = 2V
C' =
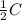
Using eqn (1):
E' =
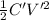
Energy, E' =
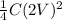
E' =
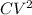 = 2E
= 2E