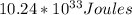Answer:
Ke=electron kinetic energy=
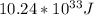
Step-by-step explanation:
The electron has a mass of
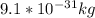
The speed of light in a vacuum is a universal constant with the value 299 792 458 m / s (186 282,397 miles / s), although it is usually close to
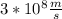
Kinetic energy (K) is the energy associated with bodies that are in motion, depends on the mass and speed of the body and is calculated using the formula:
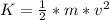 Equation(1)
Equation(1)
K=kinetic energy (J)
m =mass of the body (kg)
v= speed of the body
for this problem We replace in the equation (1)
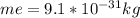 = electron mass
= electron mass
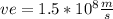 =Half the speed of light
=Half the speed of light
=electron speed
We replace in the equation (1) :
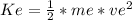
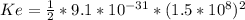
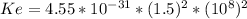
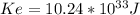
The energy kinetic of the electron is