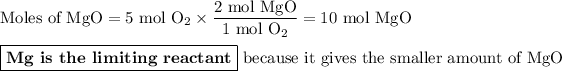Answer:
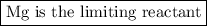
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given the amounts of two reactants, so this is a limiting reactant problem.
We know that we will need moles, so, lets assemble the data in one place.
2Mg + O₂ ⟶ 2MgO
n/mol: 2 5
Calculate the moles of MgO we can obtain from each reactant.
From Mg:
The molar ratio of MgO:Mg is 2:2
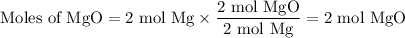
From O₂:
The molar ratio of MgO:O₂ is 2:1.