Answer:
h =12.9 w/m2 k
Step-by-step explanation:
we know that thermal conductivity of air K at 0 degree celcius = 0.024 w/mk
T_S = 80 Degree celcius
temperature gradient = -43 degree C/mm = - 43*1000 / m
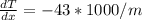
by fourier law
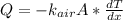
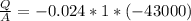
q = 1032 watt/m2
we know that from newton's law
q = h (T_s - T_∞)
1032 = h*(80 - 0)
h =12.9 w/m2 k