Answer:
adjusted COGS 1,529,500
Step-by-step explanation:
The first step, is to determinate the overhead rate
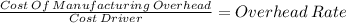
expected overhead 638,250
the company uses direct labor hour as a cost driver
labor hours expected 37,000
rate = 638,250/37,000 = 17.25
Second, we calculate the applied overhead
actual labor hours x rate
34,000 x 17.25 = 586,500
Third, we check the actual overhead
indirect labor 148,000
other cost 450,000
actual overhead 598,000
We now compare for overapplied or underapplied
586,500 - 598,000 = -11,500
The actual cost were higher, we applied less overhead
So we need to increase the cost of good sold, because the inventory sold cost was 11,500 higher than we think.
cost of goods sold 11,500
factory overhead 11,500
COGS 1,518,000
+adjustment 11,500
adjusted COGS 1,529,500