Step-by-step explanation:
According to the ideal gas equation, PV = nRT.
or, n =
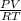
As it is given that pressure is 127 kPa or 127000 Pa (as 1 kPa = 1000 Pa), volume is 60.0
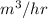 , R is gas constant equals 8.314 J/K/mol, and temperature is (490 + 273) K = 763 K.
, R is gas constant equals 8.314 J/K/mol, and temperature is (490 + 273) K = 763 K.
Hence, putting these values into the above equation as follows.
n =
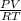
=
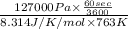
= 0.320 mol/s
Therefore, heat required will be calculated as follows.
change in enthalpy of the gas during the cooling process × mole flow
= 4.70 kJ/mol × 0.320 mol/s
= 1.50 kW
Thus, we can conclude that heat required in kW for the given situation will be 1.50 kW.