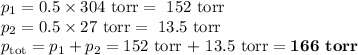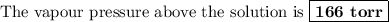Answer:
166 torr
Step-by-step explanation:
Let’s call ethane Component 1 and propane Component 2.
According to Raoult’s Law,
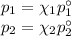
where
p₁ and p₂ are the vapour pressures of the components above the solution
χ₁ and χ₂ are the mole fractions of the components
p₁° and p₂° are the vapour pressures of the pure components.
Data:
p₁° = 304 torr
p₂° = 27 torr
n₁ = n₂
1. Calculate the mole fraction of each component
χ₁ = n₁/(n₁ + n₂)
χ₁ = n₁/n₁ + n₁)
χ₁ = n₁/(2n₁)
χ₁ = ½
χ₁ = 0.0.5
χ₂ = 1- χ₁ = 1- 0.5 = 0.5
2. Calculate the vapour pressure of the mixture