Step-by-step explanation:
It is known that relation between
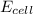 ,
,
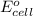 , and pH is as follows.
, and pH is as follows.
![E_(cell) = E^(o)_(cell) - ((0.0591)/(n)) * log[H^(+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ncnqhvac202vwyjazoh0v8l6o2omsvbok2.png)
Also, it is known that
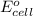 for hydrogen is equal to zero.
for hydrogen is equal to zero.
Hence, substituting the given values into the above equation as follows.
![E_(cell) = E^(o)_(cell) - ((0.0591)/(n)) * log[H^(+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ncnqhvac202vwyjazoh0v8l6o2omsvbok2.png)
0.238 V = 0 - (\frac{0.0591}{1}) \times log[H^{+}] [/tex]
![-log[H^(+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/pclsb5d5ztpswphl1czegwokhxu5hzr3m7.png) = 4.03
= 4.03
![[H^(+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/axnvi9gez4h3rovfp1qidd16ya8d7gzbon.png) = antilog 4.03
= antilog 4.03
= 3.5
As, pH =
![-log[H^(+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/pclsb5d5ztpswphl1czegwokhxu5hzr3m7.png) .
.
Thus, we can conclude that pH of the given unknown solution at 298 K is 3.5.