Answer:
average convection coefficient is 0.090597 W/m²K
Step-by-step explanation:
Given data
velocity V = 100 m/s
temperature Ts = 400 K
temperature T = 300 K
average heat flux = 20,000 W/m2
length of L = 5 m
solution
we know that heat flux that is h × ( Ts -T)
so h = 20000 / (400 - 300)
h = 200 W/m²K
and
we know Nusselt number is proportional to reynold number power to 4/5
so
Nu ∝
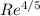
so Nu = h×L/k
so we can say
h1L1 / h2L2 =
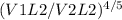
here L1 = 1m , L2 = 5m, V1 = 100 m/s and V2 = 20 m/s and h1 = 200 W/m²K
put all these value here
200(1) / h2 (5) =
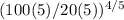
h2 = 0.090597 W/m²K
so average convection coefficient is 0.090597 W/m²K