Answer: The mass of water that must be reacted is 56.28 grams.
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
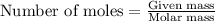 ....(1)
....(1)
Given mass of oxygen = 50 g
Molar mass of oxygen = 32.00 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
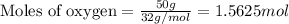
For the given chemical equation:
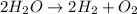
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
1 mole of oxygen is produced when 2 moles of water is reacted.
So, 1.5625 moles of oxygen is produced when =
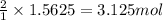 of water is reacted.
of water is reacted.
To calculate the mass of water, we use equation 1:
Moles of water = 3.125 moles
Molar mass of water = 18.01 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
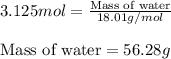
Hence, the mass of water that must be reacted is 56.28 grams.