Answer:
Value of rate constant is
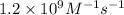
Step-by-step explanation:
![Rate=k[NH_(2)][NO]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/zalv5t6c4w0vmaygj2wx1bp2ufqxbqv2gt.png)
Here k is the rate constant of the reaction.
species inside third bracket represents concentration.
Rate constant only depends upon temperature and not on the progress of a reaction.
Here initial concentration of
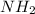 =
=
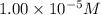
initial concentration of NO =
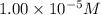
Inital rate of reaction = 0.12 M/s
So,
![k=(Rate of reaction)/([NH_(2)][NO])=(0.12)/((1.00* 10^(-5))^(2))M^(-1)s^(-1)=1.2* 10^(9)M^(-1)s^(-1)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/jfu8ual9nasdwb8cynrgj58dktxpk0rrlp.png)