Answer:
Explanation:
a) Since for any determinant we have
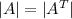
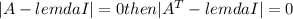
Hence both determinants would have the same eigen values
b) If A is having a zero value then by definition of eigen values we get
|A|=0. Hence we say if A is invertible if and only if A does not have a zero eigen value
c)
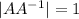
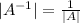
Hence eigen values of A would be the reciprocals of that of A transpose.