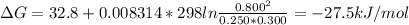Answer:
ΔG = -27.5 kJ/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
The given reaction is:
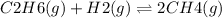
The Gibbs free energy (ΔG) is related to the standard gibbs free energy (ΔG°) as follows:
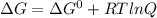
where R = gas constant
T = temperature
Q = reaction quotient
For the given reaction:
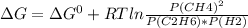
Here:
ΔG°=-32.8 kJ/mol
R = 0.008314 kJ/mol-K
T = 298 K
P(CH4) = 0.800 atm
P(C2H6) = 0.250 atm
P(H2) = 0.300 atm